Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Res Vestib Sci > Volume 20(4); 2021 > Article
-
Original Article
양성돌발성두위현훈에서 혈소판 지표의 역할에 대한 연구 -
이병민1, 임채동1, 허동구2,3, 안성기1,3

- Study on Platelet Indices in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
-
Byeong Min Lee1, Chae Dong Yim1, Dong Gu Hur2,3, Seong-Ki Ahn1,3

-
Research in Vestibular Science 2021;20(4):141-146.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21790/rvs.2021.20.4.141
Published online: December 15, 2021
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Changwon Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Changwon, Korea
3Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea
- •Corresponding Author: Seong-Ki Ahn Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, 79 Gangnam-ro, Jinju 52727, Korea Tel: +82-55-750-8178 Fax: +82-55-759-0613 E-mail: skahn@gnu.ac.kr
• Received: October 29, 2021 • Revised: November 16, 2021 • Accepted: November 22, 2021
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean Balance Society. All rights reserved.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,705 Views
- 79 Download
Abstract
-
Objectives
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is one of the most common causes of dizziness. Even though the etiology of BPPV has been widely studied, the exact mechanism remains still unclear. One of the possible factors explaining the pathophysiology of BPPV is ischemia of vestibule. In the present study, we have focused on the platelet indices including mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW), and platelet crit (PCT) to assess a risk of vestibule ischemia causing BPPV.
-
Methods
- From January 2021 to March 2021, a retrospective review was performed on 39 patients diagnosed with BPPV through vestibular nystagmography. For each platelet indices, a comparative analysis was conducted between the patient group and control group.
-
Results
- There were no significant differences when the platelet, MPV, PDW, and PCT values were compared between the study and control group. Rather, the control group showed higher PDW value than the study group.
-
Conclusions
- Ischemia of vestibule is one of the well-known causes of BPPV, but the current study showed that BPPV cannot be explained by the vestibule ischemia itself. Further studies are needed to identify the potential of ischemia regarding BPPV by approaching with other methods with a large study group.
서론
대상 및 방법
결과
고찰
결론
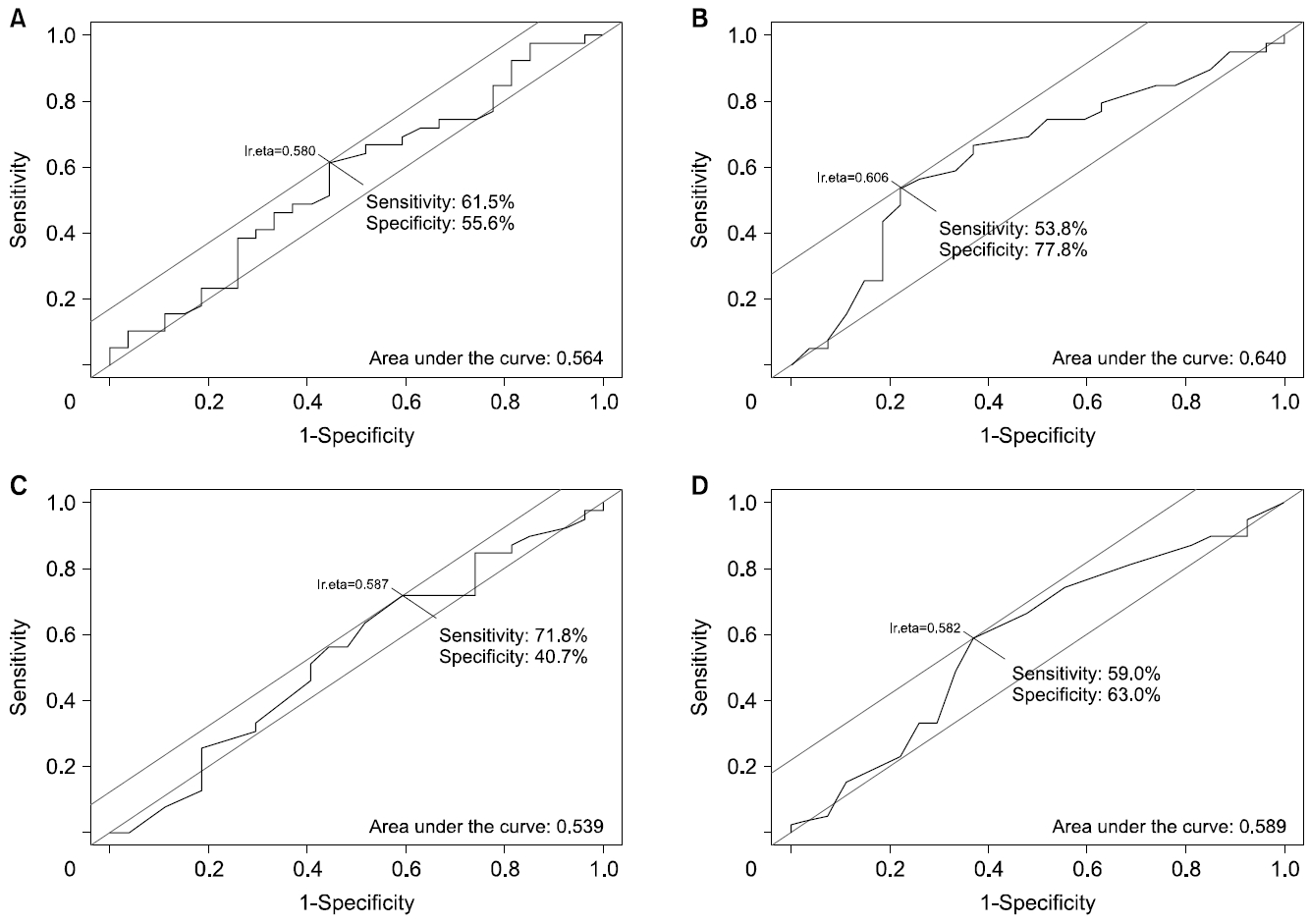
Fig. 1.Comparison of receiver operating characteristics curves of platelet (A), platelet distribution width (B), mean platelet volume (C), and platelet crit (D).


Table 1.Demographic data
Table 2.Multivariate analysis of platelet indices
- 1. Strupp M, Mandalà M, López-Escámez JA. Peripheral vestibular disorders: an update. Curr Opin Neurol 2019;32:165–73.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Brandt T, Steddin S. Current view of the mechanism of benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo: cupulolithiasis or canalolithiasis? J Vestib Res 1993;3:373–82.PubMed
- 3. Celikbilek A, Tanik N, Zararsiz G, Celikbilek M. Do platelet indices have a role in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Neurol Res 2014;36:763–8.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Wiwanitkit V. Plateletcrit, mean platelet volume, platelet distribution width: its expected values and correlation with parallel red blood cell parameters. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2004;10:175–8.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Arévalo-Lorido JC, Carretero-Gómez J, V illar-Vaca P. Mean platelet volume predicting carotid atherosclerosis in atherothrombotic ischemic stroke. Ir J Med Sci 2012;181:179–83.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Smyth SS, McEver RP, Weyrich A S, Morrell CN, Hoffman MR, Arepally GM, et al. Platelet functions beyond hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost 2009;7:1759–66.ArticlePubMed
- 7. von Brevern M, Bertholon P, Brandt T, Fife T, Imai T, Nuti D, N ewman-Toker D. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res 2015;25:105–17.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Maluf CB, Barreto SM, Vidigal PG. Standardization and reference intervals of platelet volume indices: Insight from the Brazilian longitudinal study of adult health (ELSA-BRASIL). Platelets 2015;26:413–20.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Froehling DA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, Beatty CW, Offord KP, Ballard DJ. Benign positional vertigo: incidence and prognosis in a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc 1991;66:596–601.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Katsarkas A. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): idiopathic versus post-traumatic. Acta Otolaryngol 1999;119:745–9.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Batista TR, Figueiredo RC, Rios DR. Platelets volume indexes and cardiovascular risk factors. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 2018;64:554–9.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Kaito K, Otsubo H, U sui N, Y oshida M, Tanno J, Kurihara E, et al. Platelet size deviation width, platelet large cell ratio, and mean platelet volume have sufficient sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of immune thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol 2005;128:698–702.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Park Y, Schoene N, Harris W. Mean platelet volume as an indicator of platelet activation: methodological issues. Platelets 2002;13:301–6.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Sucu M, Davutoglu V, Sari I, Ozer O, Aksoy M. Relationship between platelet indices and aortic valve sclerosis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2010;16:563–7.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Vagdatli E, Gounari E, Lazaridou E, Katsibourlia E, Tsikopoulou F, Labrianou I. Platelet distribution width: a simple, practical and specific marker of activation of coagulation. Hippokratia 2010;14:28–32.PubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Figure
- We recommend
- Related articles
-
- Canal Conversion and Reentry of Otolith in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Treatment in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Factors that Affect Successful Treatment Outcome
- The Head-Bending Test in Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- The Periodic Fluctuation of Intra-Annual Distribution of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo and Meteorological Parameters
- Intravenous Zoledronic Acid in Elderly Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo and Osteoporosis

 KBS
KBS
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite